What Are the Best Sustainable Alternatives to Plastic Packaging Bags in 2025?
Your business relies on poly bags, but international buyers demand sustainable options. Using old plastic risks losing access to key markets like the EU and alienating environmentally conscious customers.
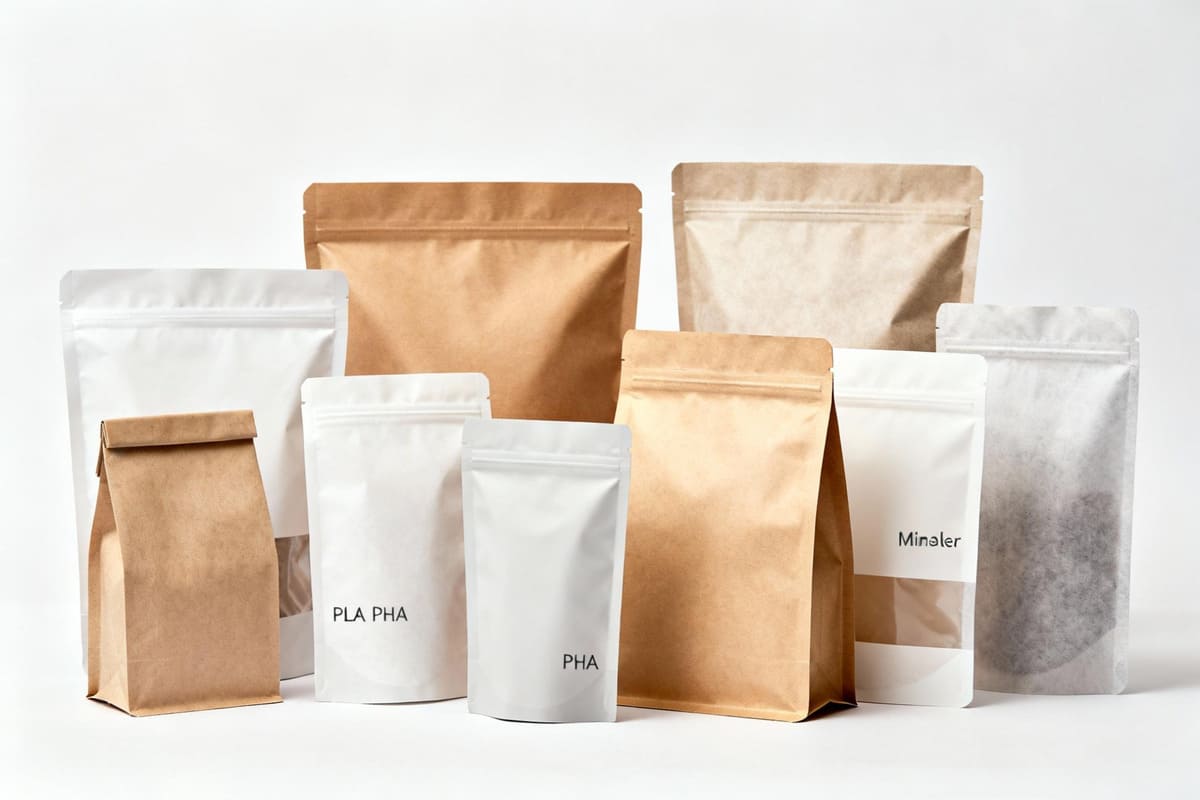
The best sustainable alternatives to plastic bags in 2025 are PLA biodegradable bags1tps://meyers.com/meyers-blog/what-is-biodegradable-packaging/)2 bags, PHA compostable films3, and laminated paper poly bags4. These options meet strict US/EU compliance standards while significantly reducing environmental impact.
<sup id=](https://whatapackaging.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/10/39-1.jpg) 5 bags including PLA, PHA, and laminated paper, displayed on a clean background" title="Sustainable Alternatives to Plastic Packaging Bags" />
5 bags including PLA, PHA, and laminated paper, displayed on a clean background" title="Sustainable Alternatives to Plastic Packaging Bags" />
A few years ago, I was working with a client who exported high-quality coffee beans to Germany. They were suddenly told their shipment was at risk of being rejected because of new EU regulations on single-use plastics6. They had an excellent product, but their packaging was about to make them non-compliant. We had to act fast. We explored several options and settled on certified PLA bags. It was a stressful process of testing, certification, and redesign. But in the end, their new packaging not only met the legal requirements but also became a huge marketing win. It taught me that these regulations aren't just hurdles; they're opportunities to improve your brand.
Are new bioplastics like PLA and PHA really better than traditional plastic?
You hear terms like "biodegradable," but you're skeptical. Can bags made from corn starch7 or bacteria really handle your products without tearing or letting moisture in, making you look unprofessional?
Yes, they are significantly better for specific applications. PLA, made from corn starch, and PHA, from bacterial fermentation8, come from renewable sources and are designed to compost, drastically reducing landfill waste.
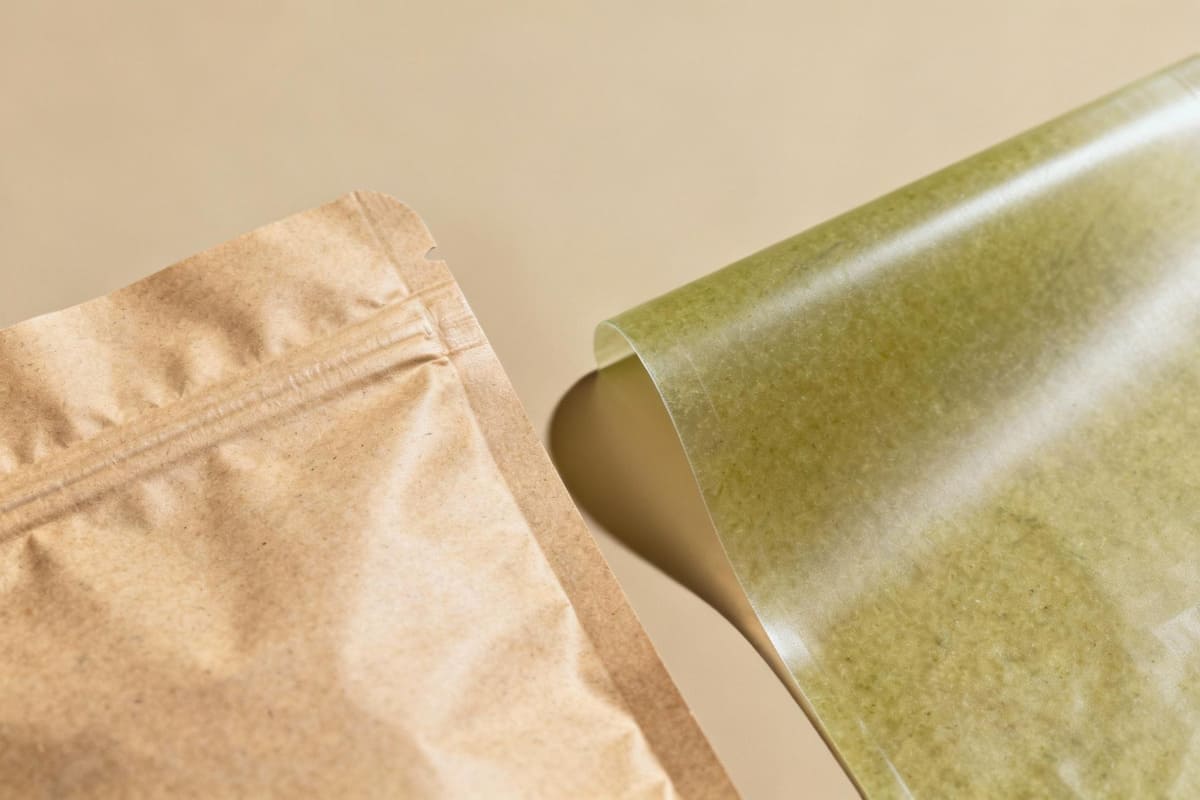

For a designer like Jacky, it's crucial to match the material to the product. These aren't just one-size-fits-all replacements for standard polyethylene. Each has its own strengths. PLA (Polylactic Acid) is fantastic for lightweight items like apparel or dry snacks. It’s semi-rigid and has a clean, professional look. It performs best when sent to an industrial composting9 facility, where it breaks down in about 90-180 days. PHA (Polyhydroxyalkanoates) is a step up in performance. It's more flexible and offers better resistance to moisture, making it a viable option for things like frozen food packaging. A huge advantage of PHA is that it can often be composted in a home compost bin10, making its end-of-life cycle much easier for the consumer. Choosing the right one depends entirely on your product's needs and your customer's access to composting.
Is a laminated paper bag a truly sustainable option?
The word "laminated" makes you think of a plastic coating. You're worried that choosing a laminated paper bag is just greenwashing, trading one problem for another and deceiving your customers.
Yes, it is a great sustainable option when made correctly. These bags combine a recyclable paper exterior11 with an ultra-thin, certified compostable film liner12, offering both a premium feel and product protection.
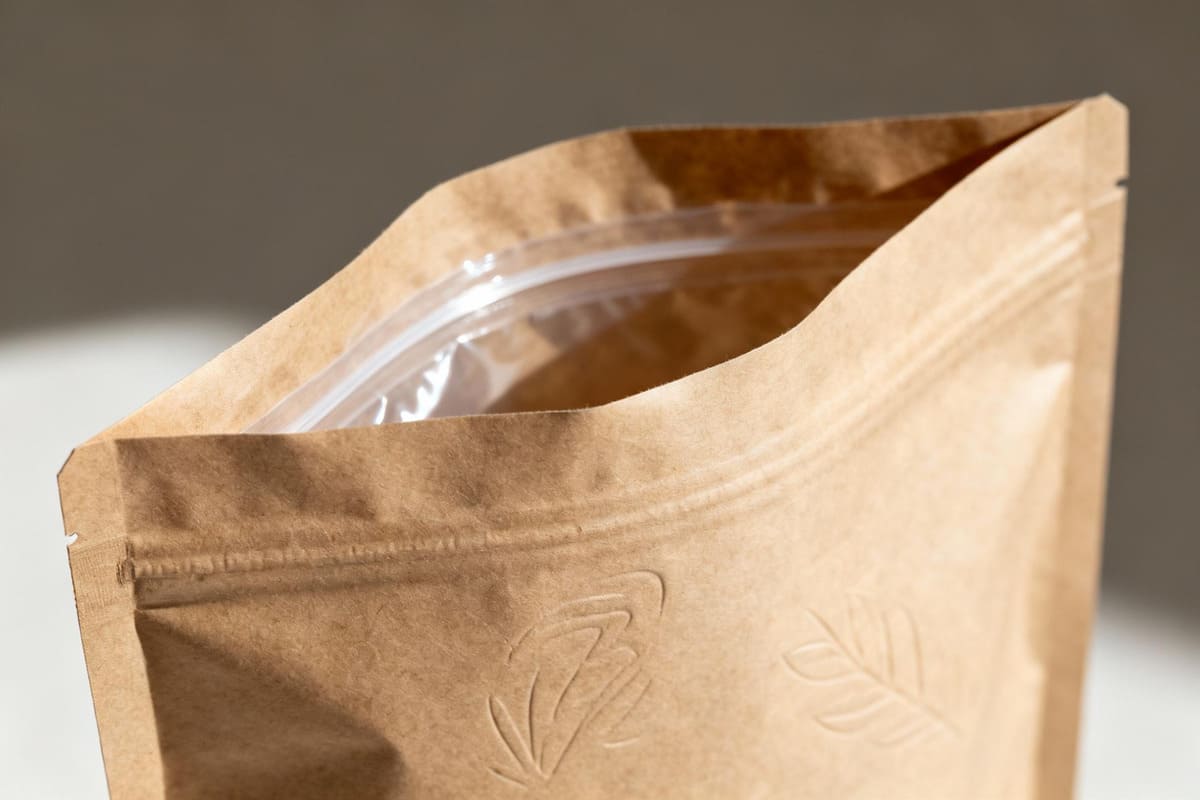

This is a common concern I hear, and it's a valid one. The key is in the details of the lamination. We aren't talking about a traditional, non-recyclable plastic coating. Modern sustainable laminated bags use a paper layer—often recycled or FSC-certified—fused with a thin interior layer of a material like PLA. This construction gives you the best of both worlds. You get the strength, structure, and premium tactile experience of paper on the outside, which is fantastic for branding. On the inside, the thin biodegradable film provides the necessary barrier against moisture or oils, protecting the product inside. I've found these bags are incredibly popular for premium goods going to markets like Japan and the UK. For a brand shipping apparel, coffee, or high-end dry goods, they communicate quality and environmental responsibility in a way that a simple poly bag can't. They are a perfect example of a hybrid solution that doesn't compromise on function or form.
You're ready to make the switch to sustainable bags. But you're worried about hidden costs, performance issues, and logistical nightmares that could derail your production and hurt your bottom line.
The main challenges are higher material costs and the need for proper disposal infrastructure. PLA and PHA require specific composting conditions that aren't available everywhere, which can complicate their end-of-life story.
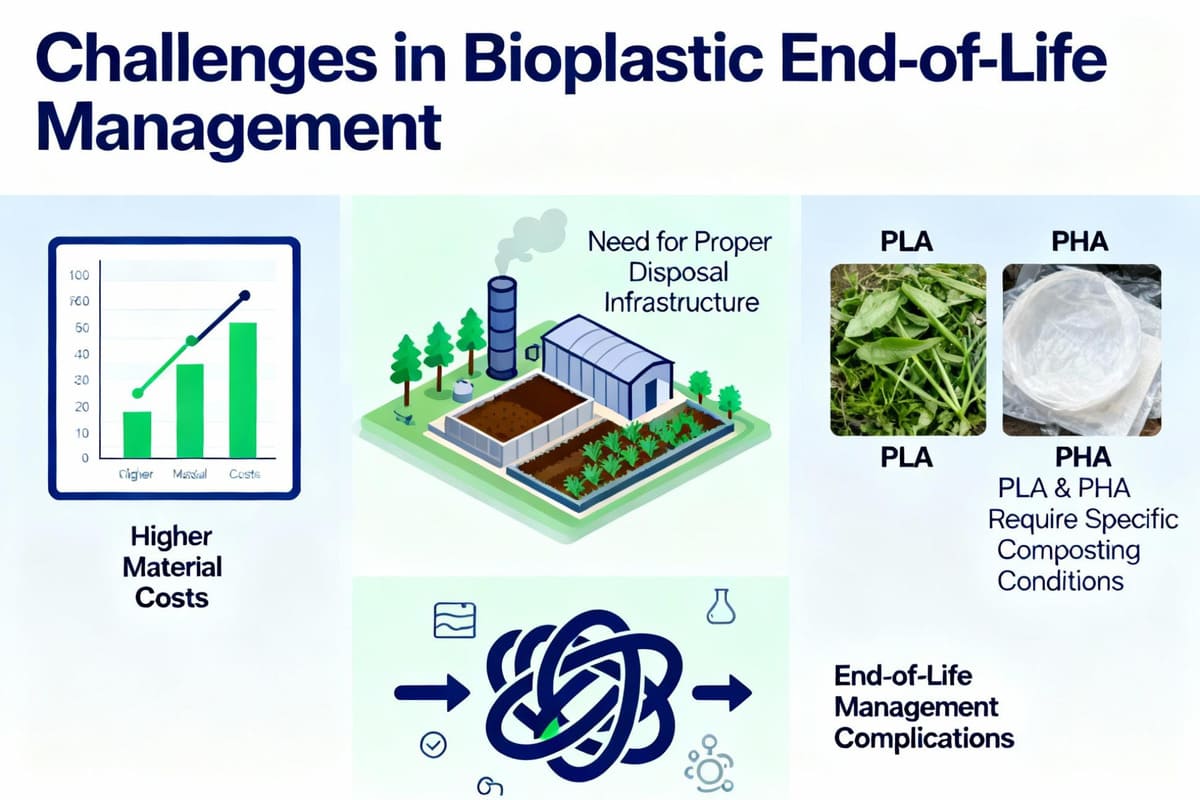
Making the change isn't as simple as swapping one bag for another. As a designer, Jacky needs to factor these practical realities into the plan. First, let's talk about cost. These advanced materials are more expensive to produce than petroleum-based plastics. You have to be prepared to either absorb that cost or justify a higher product price through strong branding that highlights your sustainable choice. Second is the end-of-life reality. You can have a fully certified compostable bag, but if your end customer lives in a city with no industrial composting facilities, that bag will likely end up in a landfill. There, it won't break down as designed. This is why it's so important to be transparent in your marketing. Instead of just saying "compostable," you might add messaging like, "Commercially compostable where facilities exist." It manages customer expectations and protects your brand from accusations of greenwashing.
How can you ensure your new sustainable supplier is legitimate?
You've found potential suppliers online offering "eco-friendly" bags. But how do you know if their claims are real? You risk importing a container of useless bags that don't meet compliance.
Always demand to see their material certifications13. For composting, this means asking for current EN1343214 (EU) or ASTM D640015 (US) certificates and verifying them with the issuing body before placing any order.

This is the most critical step for anyone importing these materials. Do not take a supplier's word for it. In my experience, legitimate suppliers are proud of their certifications and will provide them eagerly. Here is the checklist I give all my clients:
| Verification Step | What to Do | Why It's Important |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Request the Certificate | Ask for the full PDF of the EN1343214 or ASTM D640015 certificate for the specific material you are buying. | It proves the material has passed rigorous third-party testing for compostability. |
| 2. Check the Details | Verify the supplier's name, the material code, and the expiration date on the certificate. | Ensures the certificate is current and applies to your supplier and material. |
| 3. Confirm with the Issuer | Contact the certifying body (like TÜV Austria or BPI) to confirm the certificate number is valid in their database. | This is the final step to protect yourself from sophisticated counterfeit documents. |
| 4. Order a Pilot Batch | Before placing a large order, get a small batch to test its performance with your specific product. | Confirms the bag's barrier properties, strength, and sealing capabilities in a real-world scenario. |
Following these steps might seem tedious, but it protects you from costly mistakes, ensures you are truly compliant, and gives you complete confidence in your new sustainable packaging.
Conclusion
Switching to sustainable bags is a strategic investment in your brand's future. Options like PLA, PHA, and laminated paper offer compliant, functional solutions that meet modern market demands.
Explore the advantages of PLA biodegradable bags, a leading sustainable alternative to traditional plastic. ↩
Understand the term biodegradable and its implications for sustainable packaging solutions. ↩
Learn about PHA compostable films, their production process, and their environmental benefits. ↩
Discover how laminated paper poly bags combine sustainability with functionality for eco-conscious brands. ↩
Explore the advantages of adopting sustainable packaging for brand reputation and market access. ↩
Stay updated on EU regulations to ensure compliance and avoid market access issues. ↩
Find out how corn starch is transformed into eco-friendly packaging materials like PLA. ↩
Learn about the process of bacterial fermentation and its role in creating sustainable materials. ↩
Explore the process of industrial composting and its importance for biodegradable materials. ↩
Discover the benefits of PHA's compostability in home settings for eco-friendly consumers. ↩
Learn about the advantages of recyclable paper exteriors in sustainable packaging solutions. ↩
Understand the significance of certified compostable film liners in eco-friendly packaging. ↩
Learn how to ensure your packaging materials are certified and meet sustainability standards. ↩
Explore the EN13432 certification and its importance for compostable packaging compliance. ↩
Understand the ASTM D6400 certification process for compostable materials in the US. ↩




